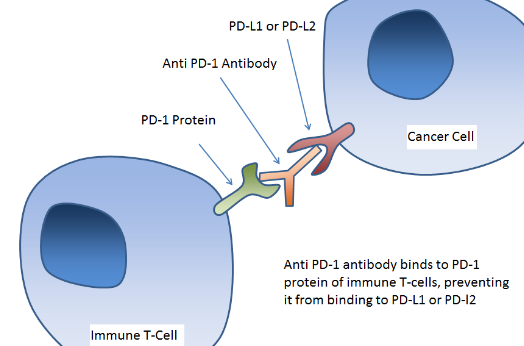
The PD-1 / PD-L1 pathway (Programmed cell death protein 1 / Programmed cell death ligand 1) is a negative regulator of the immune system that is overstimulated in certain types of cancer.
PD-1 / PD-L1 blockade is associated with a regression of tumors and today there are several drugs and clinical trials underway with anti-PD-1 and PD-L1 antibodies, known as immune checkpoint inhibitors, with a view to its application in immunotherapy against cancer.
The anti PD-1 antibodies capable of blocking this signaling pathway in vivo is a fundamental tool for cancer research in animal models . In this post we bring you a compilation of anti-PD-1 antibodies to block signaling in vivo in murine animal models.
ANTI PD-1 ANTIBODIES FOR BLOCKING SIGNALING IN VIVO
Anti-PD-1 antibodies capable of blocking PD-1 / PD-L1 pathway signaling have emerged as a promising immunotherapeutic strategy against different types of tumors such as melanoma, kidney cancer or non-small cell lung cancer, among others.
The use of these antibodies in preclinical research in vivo has become a transcendental tool. Of the multiple anti-PD-1 antibodies developed in recent years by different research groups, we highlight the monoclonal antibodies derived from the RMP1-14, 29F.1A12 and J43 clones:
- Clone RMP1-14
The generation of this clone was published first in 2003 by Takanori Kanai et to the. It was generated using the Syrian hamster BHK cells transfected with mouse PD-1 cDNA.
- Clone 29F.1A12
The generation of this clone was published first in 2003 by Spencer C. Liang et to the. It was generated using a recombinant mouse PD-1-Ig protein as antigen.
- Clone J43
The generation of this clone was published for the first time in 1996 by Agata et Yasutoshi him. It was generated using the Syrian hamster BHK cells transfected with mouse PD-1 cDNA.
In order for these antibodies to be suitable for animal research , they must meet certain specifications that are not usually common in antibodies for in vitro immunoassays such as:
- Contain very low endotoxin level (<2 EU / mg)
- High purity (> 95%)
- Be free of murine pathogens
- Be Azide Free
- Free of compounds that can interfere in in vivo tests , such as preservatives, stabilizers, etc.
- Presented in high concentrations (˃1mg / ml)
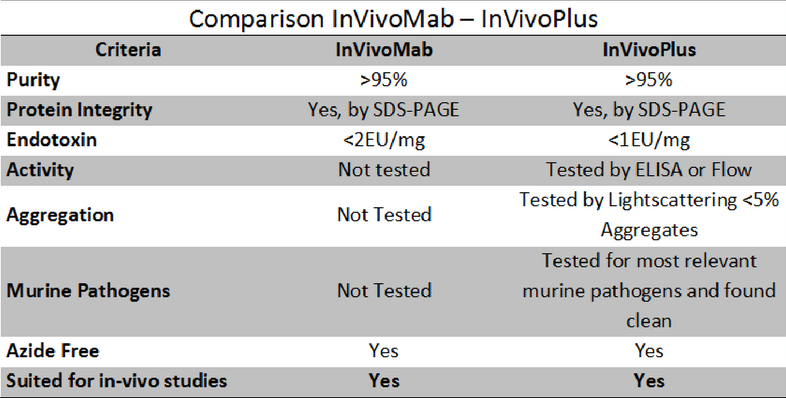
Based on these specifications, we found two types of antibodies for in vivo research : InVivoMAb and InVivoPlus.
The following table describes the differences between the two:
To finish, we leave you with a compilation of some of the most used anti-PD-1 antibodies to block signaling of this route in murine animal models :
- BE0146
- Anti-Mouse PD-1 (CD279)
- InVivoMAb
- Clone RMP1-14
- BP0146
- Anti-Mouse PD-1 (CD279)
- InVivoPlus
- Clone RMP1-14
- BE0273
- Anti-Mouse PD-1 (CD279)
- InVivoMAb
- Clone 29F.1A12
- BP0273
- Anti-Mouse PD-1 (CD279)
- InVivoPlus
- Clone 29F.1A12
- BE0033-2
- Anti-Mouse PD-1 (CD279)
- InVivoMAb
- Clone J43
- BP0033-2
- Anti-Mouse PD-1 (CD279)
- InVivoPlus
- Clone J43